Using the material builder
The material builder allows you to define an absorber based on its construction and let Treble calculate the corresponding impedance and absorption values. It is currently in beta and will be improved and expanded upon in the near future. This first iteration of the builder allows for the calculation of normal incidence impedance of porous absorbers on a rigid backing. Following is an explanation of the components in the view:
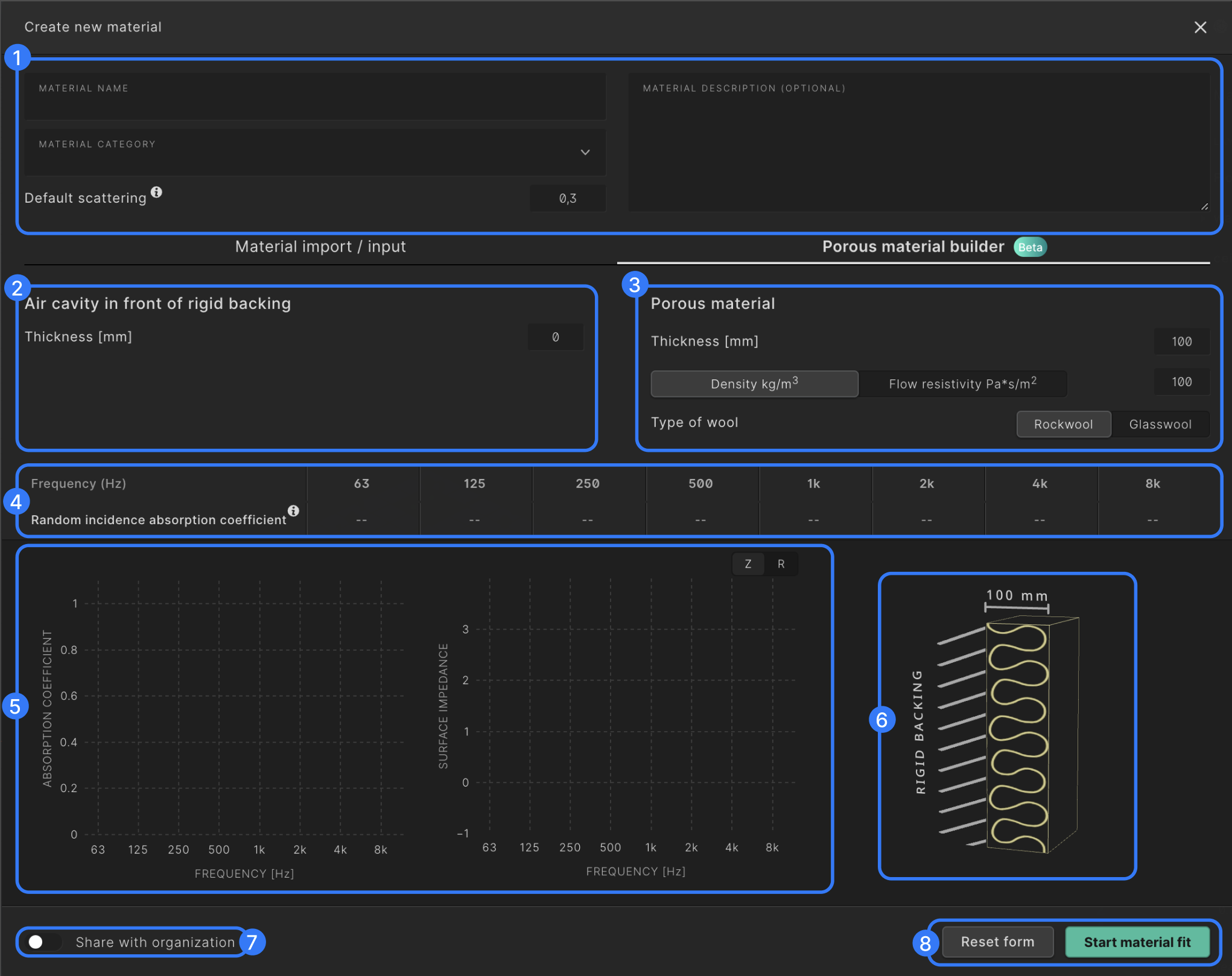
-
Here you can name and categorize the material in order to be able to find and filter it during the material assignment step of a simulation setup. Here you can also set the default scattering value of your material. For the best results when setting a scattering coefficient we recommend consulting following guide.
-
Here you can set the depth of the air cavity in mm.
-
Here you can set the thickness of the porous absorber in mm. You can then either specify the flow resistivity of the material or the density and wool type. For the latter Treble estimates the corresponding flow resistivity to use in calculations.
-
In this table the random incidence absorption coefficient of the setup will be defined after the material fit has been started.
-
The graph on the left shows the random incidence absorption coefficient of the setup after the material fit has been started. The graph on the right can be toggled between the normal incidence surface impedance and the normal incidence reflection coefficient. The yellow lines represent the data you input. The green lines represent the data our solver uses after going through our vector fitting step.
-
The figure displays your current setup.
-
This toggle allows you to share the material with everyone in your organization so that it will be displayed for everyone in their material library.
-
When you’ve inputted your data, selecting this button will start the material fitting process. The fitter will construct a continuous function to represent the reflection coefficients as this is needed for the wave-based solver.
After selecting the ‘Start Material fit’ the button changes to ‘Create material’ If you’re happy with the results you can select ‘Create material’ to store the material in your material library. If you want to make changes to the material and run the fitting process again you can select ‘Edit’
Currently the material builder calculates the impedance for normal incidence only. The random incidence absorption coefficient is then found by applying the Paris formula, assuming a local reaction.
The materials in our material database have been computed with angle averaged impedance values taken into account. There can therefore be differences between the results you get out of the material builder and the predefined materials in our library when comparing the same setup between the two. Angle averaged impedance values is something we will explore in future versions of the material builder.
You can read more about the theory behind the material builder in the Material Builder - Theory Section.